Bed rails are safety devices that can help prevent falls from bed.
They serve as protective barriers to prevent accidental falls during sleep or while getting in and out of bed.
Bed rails benefit the elderly, children, individuals with disabilities, and hospital patients.
Yet, along with knowing their benefits and risks, it is also important to know the different types of bed rails and their distinct features.
Types of Bed Rails Overview
Let’s delve first into the three main categories of safety bed rails: integral bed rails, third-party bed rails, and hospital bed rails.
Differentiating each type helps you in choosing bed rails for your needs.
Let’s explore these categories in detail:
1. Integral Bed Rails

Integral bed rails are types of bed rails incorporated into the design of the bed itself.
They are either supplied with the bed as a standard feature or offered as an optional accessory by the bed manufacturer.
Integral bed rails have several advantages:
- Enhanced security – Less likely to be dislodged as it is attached to the bed frame.
- Reduced tripping hazard – Flush with the bed; they reduce tripping and catching hazards.
- Aesthetic appeal – They blend in with the bed for a more aesthetically pleasing look.
However, integral bed rails also have some disadvantages:
- Higher cost – They can be more expensive due to their built-in design.
- Availability limitations – Not all bed frames come with integral bed rails.
- Installation challenges – Can be difficult to install, especially for DIY beginners.
2. Third-Party Bed Rails

Third-party bed rails are not specific to any particular model of bed. Plus, they are a good option for people who need a temporary or adjustable bed solution.
Plus, being the best bed rail type to some, it can be installed between the mattress and the box spring.
Here are some of the advantages of third-party bed rails:
- Affordability – Third-party bed rails typically cost less than other bed rail handles
- Versatility – Available in wider bed rail models, therefore, better bed compatibility.
- Ease of installation – They can be the best bed rail type due to their easy installation.
However, third-party bed rails also have some disadvantages:
- Security- Risky if the bed rails attached to the bed frame are not checked.
- Aesthetics – More noticeable as they are not integrated into the bed.
- Limited portability – Usually mounted at a single fixed point.
3. Hospital Bed Rails
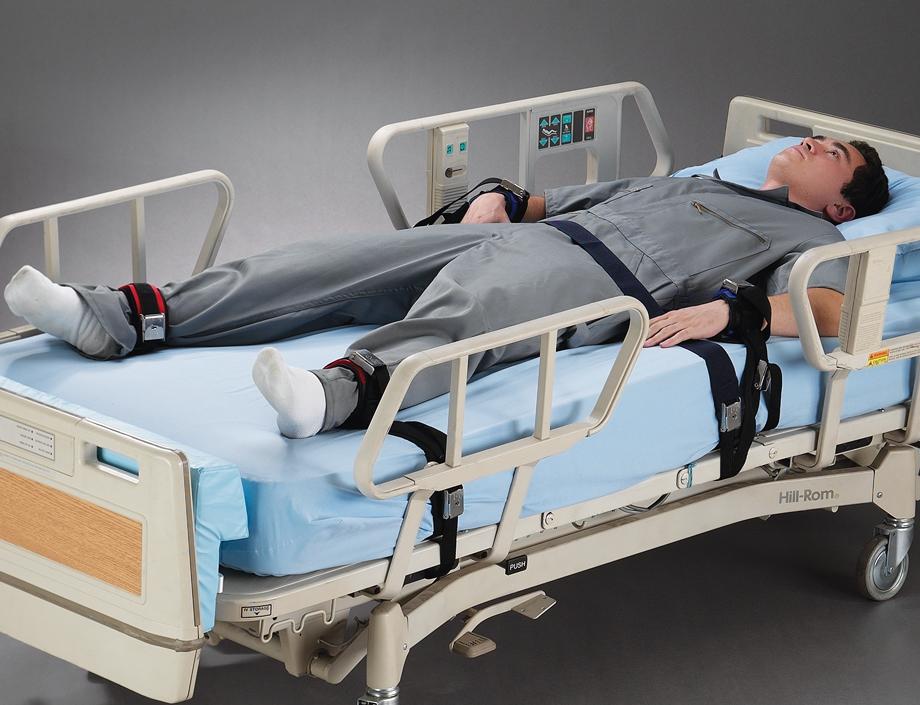
Hospital bed rails are designed for medical settings, providing enhanced patient safety features.
They help secure a patient to the bed rail handles with a safety strap, and they’re often attached to adjustable beds.
These bed rails usage in nursing homes are also common.
Here are some of the advantages of bed rails in hospital beds:
- Adjustable – Offer adjustable bed height options for customization.
- Convenient – Easy to install and remove.
- Safety – Equipped with enhanced safety features.
- Strict compliance with guidelines – Adheres to medical bed standards.
However, hospital bed rails also have some disadvantages:
- Safety hazards – If not used properly, they can potentially cause injuries.
- Restriction of movement – They can limit patients’ mobility.
- Discomfort – Uncomfortable if the rails or hospital beds are made of hard materials.
Expense – Hospital bed rails can be costly, especially if not covered by insurance.
Portable Bed Rails for Children
Portable bed rails help keep children safe, especially when transitioning from a crib. They can prevent children from rolling out of bed, which can help to prevent injuries.
Many portable bed rails, including mesh, swing-down, and foam bumpers, are available.
1. Mesh Bed Rails

These bed rails are made of breathable mesh material that offers a secure barrier while maintaining good airflow.
This means that they allow air to circulate, which can help to prevent children from sweating or getting too hot at night.
They are lightweight, easy to install, and often foldable for convenient storage and travel.
However, a mesh bed rail is not recommended for children under 18 months due to the risk of entrapment, climbing, or asphyxia
2. Swing-Down Bed Rails

Swing-down bed rails are a type of support rail that can be folded down when not in use — a good option for travel.
Also known as fold-down bed rails, they are ideal and safer for children who can get in and out of bed easier.
These bed rails feature a hinge mechanism that allows them to swing down, providing convenient access to the bed.
Vertical legs on this bed rail transfer weight to the floor when standing.
3. Foam Bumpers

Foam bumpers are a safe and effective way to prevent children from rolling out of any regular bed.
They are affordable and readily available. They are comfortable enough to support legs resting on the floor.
Foam bumpers are portable side rails that provide children with a soft and cushioned barrier.
They can cause entrapment if incorrectly positioned or if the child moves during sleep. So regularly monitor your child’s sleeping position and adjust the bumper if necessary.
Portable Bed Rails for Adults
These suitable bed rails for elderly individuals are safety devices that help keep a patient safe while in bed.
There are also three portable bed rails for seniors: assist rails, stand-up assist rails, and height-adjustable bed rails.
Nonetheless, these safety rails come in various styles, made of metal or plastic, and attached to the side of standard beds.
1. Assist Rails
Assist rails are the most basic type of bed rails for seniors.
They are typically low to the ground and provide a soft barrier to prevent adults from rolling out of bed.
Some of these rails come with support legs, while others do not. Some have two support legs that rest on the floor and a horizontal rail that slips between mattresses.
Whether you prefer having only one-bed rail or dual bed rails, they are ideal for adults at risk of bed falls.
Assist rails for adults are typically designed with a height ranging from 18 to 24 inches and a width ranging from 24 to 36 inches.
2. Stand-Up Assist Rails
Stand-up support rails are a good option for adults with difficulty getting in and out of bed.
They are portable bed rails designed to give additional support and help adults transition from sitting to standing.
These bed assist rails are taller than regular assist rails and have a bed handle that adults can use to easily pull themselves up from bed.
Stand-up support rails are usually 24-30 inches high and 24-36 inches wide.
3. Adjustable Height Rails
Height-adjustable rails cater to individuals of different heights and needs, as they can be easily adjusted. This makes an adjustable bed assist rail a versatile option.
They have user-friendly height adjustment mechanisms for quick customization.
With adjustable height rails, it can easily adapt its position to cater to different preferences and specific needs.
Adjustable length bed rails range from 18 to 30+ inches in height and 24 to 36 inches in width.
Hospital Bed Rail Terminology
It’s important to understand the terminology associated with different types of rails.
Knowing these ensure a better understanding of the types of bed rails and observance of bed rail safety.
1. Full-Length Rails
A full-length bed rail is the most common type of hospital bed rail. They can be either fixed or adjustable.
A full-length dual bed rail makes it easier for a user sleeping on an alternating-pressure air mattress to turn from side to side.
Although fixed full-length rails cannot be moved, the adjustable ones can be raised or lowered.
FEATURES
- Length: Extend to the entire length of the bed frame
- Purpose: Prevent patients from falling out of bed on either side
- Advantage: Provide the most comprehensive protection
- Disadvantage: A full-length rail can make it hard to get in and out of bed safely.
2. Half-Length Rails
Half rails can be a valuable safety feature for hospital beds and healthcare patients.
This type is a bed safety rail option for patients who can get in and out of bed independently but still need extra support.
They also assist in standing out of bed and facilitate changing sleeping positions throughout the night safely.
FEATURES
- Length: Extend from the headboard to the middle of the bed frame
- Purpose: Prevent patients from falling out of bed on one side
- Advantage: Provide a good balance of protection and mobility
- Disadvantage: It may not provide enough protection for king-size beds
3. Telescopic Rails
Telescopic bedside rails are often found in hospital bed rails. They can be extended or retracted to different lengths.
Good thing, especially if you want to avoid bed rails that require the patient to climb over them to get in and out of a hospital or medical bed.
This makes a telescoping rail the most versatile option for patients needing varying support levels.
FEATURES
- Length: adjustable bed rails length
- Purpose: provide support for patients
- Advantage: offer the most flexibility
Disadvantage: it can be more expensive than crossbar bed rails or legless bed rails.
Alternatives to Traditional Bed Rails
A bed rail is also known as a bed assist or safety rail. They support and prevent falls when getting in and out of bed, transferring, or moving around.
Most bed rails in traditional home-style beds are a common safety measure for preventing falls, but they can also hinder some.
For these reasons, some people seek alternatives to traditional bed rails.
1. Safety Netting
Safety netting is one alternative to a traditional bed rail.
It is a mesh barrier that is placed around the bed. It also offers a flexible and breathable solution for bed safety, even when used on legless bed rails.
Plus, built-in storage from some models.
Safety netting is a good option for people who need fall protection but not full-height rails.
2. Low-Height Beds
Low-height beds are designed to minimize the distance between the mattress and the floor.
They offer additional support against falls without installing rails or multiple horizontal cross bars.
For wheelchair users, a legless bed rail or these low-height beds are usually the best bed rails to consider.
3. Positional Wedges
Positional wedges are also a good alternative to traditional bed rails.
Some positional wedges are designed to help people keep their heads elevated.
Unlike full-length bed rails, positional wedges offer a non-restrictive alternative. They provide support without enclosing the individual.
Like dual bed rails, these can provide safety, even if used on a dual bed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Properly understanding the ins and outs of this topic helps ensure safety and comfort, especially in purchasing bed rails.
Here are some FAQs related to the types of bed rails that our team has gathered.
What Is the Purpose of Bed Rails?
Adjustable bed rails prevent falls and injuries in acute, community, and home care settings. They help reduce fall risk for people with balance or mobility issues.
Adjustable bed rails can be an alternative to restraints in medical or care settings. But only for individuals needing containment or protection from unintended harm.
Using bed rails as restraints requires valid justifications; otherwise, you will face a lawsuit.
How Do I Choose the Right Type of Bed Rail for My Needs?
Consult with a healthcare professional or caregiver before using adjustable bed rails to make the best decision for your situation.
They can help you assess your risk of falls and recommend the best bed assist rail for you.
Check compatibility with bed frames, mattress heights, and mattress widths before you purchase bed rails.
Not all bed rails fit all standard bed types, so it’s important to check for proper and safe fit and weight capacity.
Are Bed Rails Safe for Babies and Toddlers?
The US Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) recommends only using bed rails for children aged 2 to 5.
Before installing a bed rail, your child should be able to independently climb out of an adult-sized bed.
Consider using a toddler or lower-to-the-ground toddler floor bed if they have difficulty.
Follow safe sleep guidelines and use appropriate sleep environments for babies and toddlers.
Do I Need a Prescription for a Hospital Bed Rail?
In most cases, you do not need a prescription to buy hospital rails. Hospital rails are considered Durable Medical Equipment (DME), and DME does not require a prescription.
But, take note that health agencies have provided guidelines where this does not apply. (check the next FAQ for these guidelines)
You may need a prescription from your doctor for hospital rails for children under two or those with medical conditions.
Medicare insurance may also require a prescription to have the cost of the hospital bed rails covered.
What Are the Regulations Surrounding Bed Rail Safety?
Bed rail safety regulations can differ from country to country or state to state.
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) regulates medical devices in the UK.
They guide the safe use and proper installation of bed rails and report adverse incidents or defects related to these devices.The Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC) and Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have set safety standards for bed rails in the United States.
Conclusion
To improve the quality of life, especially in one’s senior years, knowing bed rail safety concerns for elderly individuals is essential.
Falls are common and can cause chronic pain among seniors. Good thing bed rails can prevent falls and their lifelong consequences.
Nonetheless, it is equally important to remember that bed rails are not a substitute for adult supervision.
People who use bed rails should always be supervised, especially those disoriented or with dementia.
The rule is simple. Research how bed rails work and read reviews to make an informed decision.



