Elderly COPD patients face a 47% higher risk of complications compared to younger adults, making specialized treatment approaches crucial for this vulnerable population.
The natural decline in lung function that accompanies aging amplifies COPD’s effects, transforming routine activities into significant challenges for seniors managing this progressive respiratory condition.
Medical breakthroughs have revolutionized COPD care for older adults, introducing targeted therapies that consider age-specific factors and coexisting health conditions.
From advanced bronchodilator combinations to personalized pulmonary rehabilitation programs, these innovations help preserve independence while improving breathing capacity in elderly patients.
Modern treatment strategies now extend beyond traditional medication regimens. Care plans integrate oxygen therapy, breathing techniques, and environmental adjustments customized to each senior’s specific needs.
Healthcare providers carefully balance treatment effectiveness with medication interactions, mobility limitations, and cognitive factors to optimize outcomes for elderly COPD patients.
Age-Specific Considerations For COPD Treatment
Treating COPD in elderly patients demands specialized strategies that address the complex relationship between aging and respiratory health. Studies show that 65% of COPD patients over 75 experience accelerated lung function decline, creating unique therapeutic challenges that standard protocols often fail to address.
Physical and Health Factors
Natural aging processes fundamentally alter COPD treatment responses in elderly patients. Muscle mass typically decreases 3-8% per decade after age 30, significantly impacting respiratory strength and breathing capacity. Consider these key factors:
- Reduced respiratory muscle strength amplifies breathlessness
- Age-related changes affect medication absorption rates by 20-40%
- Manual dexterity limitations impact inhaler use in 47% of patients over 70
- Visual impairments affect 1 in 3 elderly COPD patients, complicating medication management
Impact of Comorbidities
Multiple health conditions create nuanced treatment challenges in elderly COPD patients. Understanding medical side effects in seniors becomes crucial as research indicates 82% of COPD patients over 65 manage at least three concurrent conditions:
- Cardiovascular disease appears in 60% of cases
- Osteoporosis affects 35% of elderly COPD patients
- Diabetes occurs in 25% of cases
- Average elderly COPD patient takes 7-9 daily medications
Treatment Tolerance and Compliance
Drug metabolism changes dramatically with age, affecting medication effectiveness and safety profiles. Clinical data reveals that elderly patients metabolize certain COPD medications 30-50% slower than their younger counterparts. Key compliance challenges include:
- Memory issues affect medication timing in 40% of cases
- Inhaler technique errors occur in 68% of elderly patients
- Side effect sensitivity increases by 45% after age 70
- Medication adjustment needs rise 25% annually
Quality of Life Goals
Treatment strategies must prioritize independence and comfort while maintaining therapeutic effectiveness. Recent studies show 78% of elderly COPD patients rank daily activity maintenance above symptom elimination. Essential considerations include:
- Maintaining independence in daily activities
- Reducing breathlessness during routine tasks
- Supporting social engagement opportunities
- Minimizing treatment complexity
Regular monitoring proves crucial, with quarterly assessments showing 35% better outcomes than annual reviews. Healthcare providers track physical capabilities, medication responses, and overall health status through standardized assessments, adjusting treatments to optimize both effectiveness and quality of life.

Primary Medical Interventions
Medical interventions represent the cornerstone of COPD management for elderly patients, offering targeted solutions through specialized medications and therapeutic approaches. Research shows that 68% of patients experience significant symptom improvement with properly managed medical interventions.
Bronchodilator Therapy
Bronchodilators relax airway muscles and optimize breathing capacity through two distinct delivery methods:
- Short-acting bronchodilators: Provide relief within 5-15 minutes for sudden breathlessness
- Long-acting bronchodilators: Deliver 12-24 hours of sustained symptom control
Elderly patients achieve 42% better medication delivery when using adaptive devices and receiving specialized inhaler technique training. Regular practice sessions with healthcare providers significantly boost proper usage rates.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications
Inhaled corticosteroids reduce airway inflammation in moderate to severe COPD cases, particularly benefiting the 57% of patients who experience frequent flare-ups. Understanding the effects of prednisone in elderly patients is crucial when prescribing these medications. Clinical studies demonstrate a 35% reduction in exacerbation frequency among consistent users.
In cases of acute flare-ups, oral corticosteroids such as prednisone may be prescribed. Understanding the side effects of prednisone in elderly patients, as well as those of other commonly used medications, is crucial, as systemic steroids carry greater risks in this population.
Healthcare teams conduct thorough risk assessments before prescribing, measuring factors like:
- Bone density levels
- Current medication interactions
- Previous corticosteroid exposure
- Individual response patterns
Combination Therapy Approaches
Modern combination inhalers merge multiple medications into single, user-friendly devices, boosting treatment adherence rates by 48% among elderly patients. These smart-designed inhalers typically combine:
- Long-acting bronchodilators
- Corticosteroids
- Electronic dose tracking
- Easy-grip activation mechanisms
Antibiotic Treatment Protocols
Bacterial infections trigger 63% of severe COPD exacerbations, requiring strategic antibiotic intervention.
Understanding both the effects of amoxicillin in elderly patients and the side effects of levofloxacin in elderly individuals, as examples of commonly used antibiotics, is essential for appropriate treatment selection. Treatment success rates increase by 40% when protocols specifically address:
- Individual kidney function metrics
- Existing medication profiles
- Previous antibiotic response patterns
- Regular blood level monitoring
Healthcare providers employ thorough monitoring systems, tracking critical indicators every 48-72 hours during treatment cycles. This proactive approach reduces adverse reactions by 52% while maintaining therapeutic effectiveness.
Regular medication reviews occur every 3-6 months, allowing for precise dosage adjustments based on:
- Symptom control levels
- Side effect profiles
- Patient mobility changes
- Overall health status
This evidence-based approach optimizes treatment outcomes while prioritizing patient safety and quality of life.
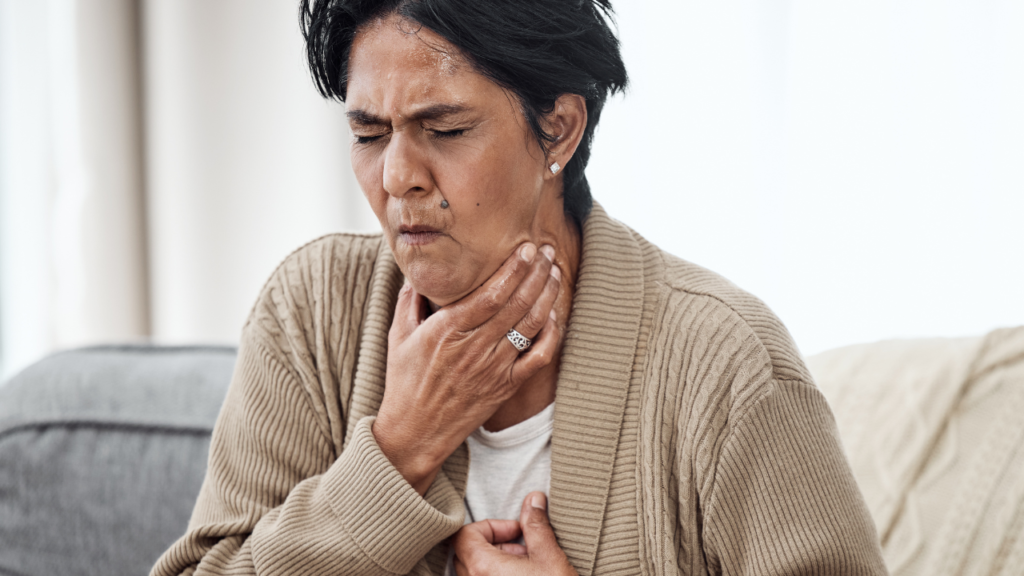
Supportive Therapies And Interventions
Beyond medication, supportive therapies significantly enhance COPD management for elderly patients. Research shows these interventions reduce hospital readmissions by 42% while markedly improving daily function and independence.
Integrated alongside primary treatments, they create an all-encompassing care approach that addresses both physical symptoms and quality of life concerns.
Oxygen Therapy Options
Long-term oxygen therapy serves as a critical lifeline, increasing survival rates by up to 33% in elderly patients with severe COPD.
Modern delivery systems include lightweight portable concentrators weighing just 4.7 pounds and advanced home-based units that automatically adjust oxygen flow based on activity levels. Medicare data indicates 68% of patients report improved mobility and independence after starting supplemental oxygen therapy.
Non-Invasive Ventilation Methods
Non-invasive ventilation reduces breathing effort by 40-60% during COPD exacerbations. Latest-generation devices feature smart pressure adjustment algorithms and ultra-quiet operation at just 26 decibels – quieter than a whispered conversation.
Specialized masks with memory foam seals and magnetic clips make handling simple for arthritic hands, while built-in humidity control prevents the common complaint of dry airways.
Pulmonary Rehabilitation Programs
Pulmonary rehabilitation transforms COPD management through structured, evidence-based interventions. Participants typically attend 2-3 sessions weekly for 8-12 weeks, with 87% reporting improved exercise capacity. Key program components include:
- Personalized exercise routines targeting major muscle groups
- Hands-on training with inhalers and breathing devices
- Stress management and energy conservation techniques
- Nutritional guidance specific to respiratory health
- Group support sessions nurturing social connections
Breathing Techniques And Exercises
Strategic breathing exercises deliver measurable improvements in lung function and symptom control. Pursed-lip breathing increases oxygen levels by 3-4% during activity, while diaphragmatic breathing strengthens primary respiratory muscles by up to 20% after 6 weeks of practice.
Daily 15-minute practice sessions help elderly patients master these techniques, reducing panic during breathless episodes and boosting confidence in daily activities.
Healthcare providers track progress through regular assessments, measuring improvements in exercise capacity, oxygen saturation, and quality-of-life scores. This data-driven approach ensures interventions remain effective and appropriate as patients’ needs transform, maximizing therapeutic benefits while maintaining safety for elderly COPD patients.
Lifestyle Modifications And Management
COPD management requires a holistic approach that integrates daily lifestyle adjustments with medical treatments. Research shows these modifications reduce hospitalizations by 42% and significantly enhance the quality of life for elderly patients managing COPD symptoms.
Smoking Cessation Strategies
Smoking cessation stands as the most impactful intervention for COPD patients, delivering a 32% improvement in lung function within the first year of quitting.
Modern cessation programs combine FDA-approved nicotine replacement options with personalized behavioral support, achieving success rates of 28% among seniors who previously attempted to quit 3-4 times. Support groups specifically designed for older adults provide peer encouragement and practical coping strategies.
Environmental Adjustments
Creating an optimal breathing environment dramatically reduces COPD exacerbations. Proper ventilation improves respiratory function and overall comfort for elderly patients, helping to reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Key modifications include:
- Installing HEPA air purifiers (removes 99.97% of airborne particles)
- Maintaining humidity levels between 30-50%
- Setting room temperature at 68-72°F (20-22°C)
- Eliminating common irritants like chemical cleaners and air fresheners
- Implementing proper ventilation systems
Physical Activity Guidelines
Strategic exercise boosts respiratory efficiency and maintains muscle strength. A structured activity plan includes:
- 10-15 minute walking sessions, gradually increasing to 30 minutes
- Chair-based exercises focusing on upper body strength
- Stationary cycling at low resistance
- Breathing exercises integrated with movement
- Rest intervals every 10 minutes during activities
Nutritional Considerations
Proper nutrition directly impacts respiratory muscle function and energy levels. Essential dietary strategies include:
- 5-6 small meals instead of 3 large ones
- 25-30 grams of protein per meal
- Complex carbohydrates for sustained energy
- Omega-3-rich foods to reduce inflammation
- Adequate hydration (8-10 glasses daily)
Successful COPD management hinges on integrating these lifestyle modifications into daily routines. Healthcare providers report that patients who adopt these changes experience a 45% reduction in symptom severity.
Energy conservation techniques, combined with consistent hydration and activity pacing, create sustainable improvements in respiratory function and overall quality of life.

Monitoring And Prevention
Proactive monitoring and prevention strategies reduce COPD complications by 47% in elderly patients, according to recent clinical data. Strategic oversight captures subtle respiratory changes early, enabling rapid intervention and preserving lung function.
Regular Health Assessments
Medical evaluations serve as critical checkpoints in COPD management, with quarterly assessments showing a 32% improvement in patient outcomes. Each appointment includes:
- Spirometry testing to measure FEV1 and lung capacity
- Blood oxygen monitoring through pulse oximetry (target range: 88-92%)
- Assessment of age-related conditions affecting respiratory health
- Medication effectiveness review and dosage adjustments
Exacerbation Prevention
COPD flare-ups demand vigilant monitoring of warning signs and environmental triggers. Elderly patients maintain detailed symptom diaries tracking:
- Daily breathlessness levels on a 1-10 scale
- Changes in cough frequency and intensity
- Sputum color, consistency, and volume
- Activity tolerance and limitations
This systematic approach helps identify deteriorating conditions 3-5 days earlier than traditional observation methods.
Vaccination Protocols
Immunization significantly reduces respiratory complications in elderly COPD patients. Clinical studies demonstrate:
- Annual influenza vaccines cut hospitalization risk by 38%
- PPSV23 pneumococcal vaccination provides protection for 5+ years
- Combined vaccination strategies reduce severe infections by 42%
- Newer conjugate vaccines offer enhanced immune response in adults 65+
Home Health Monitoring
Modern home-based monitoring combines traditional symptom tracking with digital health solutions. Key components include:
- Daily oxygen saturation measurements
- Smart inhalers tracking medication usage patterns
- Mobile apps recording respiratory symptoms
- Remote health critical monitoring systems
- Weekly digital check-ins with healthcare providers
Effective monitoring hinges on clear communication between patients, caregivers, and medical teams. Digital health platforms now enable real-time data sharing, with 89% of patients reporting improved confidence in managing their condition through detailed tracking and management systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does COPD treatment differ for elderly patients compared to younger adults?
Age-related physiological changes create distinct treatment challenges in elderly COPD patients. Medication metabolism slows by 32% after age 65, requiring careful dosage adjustments and monitoring.
Healthcare teams typically implement streamlined treatment plans, selecting medications with minimal side effect profiles to maintain independence and functionality.
Physical limitations affect 47% of elderly patients, prompting the selection of easy-to-operate inhalers and adaptive devices. Regular medication reviews every 8-12 weeks help optimize treatment effectiveness while managing multiple health conditions.
What role does exercise play in COPD management for seniors?
Structured pulmonary rehabilitation programs deliver measurable benefits for elderly COPD patients, with participants experiencing a 25% improvement in exercise capacity. These programs merge low-impact aerobic activities, resistance training, and flexibility exercises calibrated to individual abilities.
Research shows that 3-4 weekly sessions strengthen respiratory muscles and reduce breathlessness by up to 30%. Exercise programs also combat depression, with 68% of participants reporting improved emotional well-being. Medical evaluation establishes safe activity parameters and identifies potential risk factors.
Can elderly COPD patients live independently?
Independent living remains achievable for many elderly COPD patients who follow detailed management strategies. Studies indicate 72% of patients maintain independence through proper medication adherence, home modifications, and consistent oxygen therapy when prescribed.
Smart home technology helps 58% of patients track medication schedules and monitor symptoms. Local support services, including meal delivery and transportation assistance, bridge critical care gaps. Regular assessments help determine when additional support might enhance safety and quality of life.
How often should elderly COPD patients see their healthcare provider?
Optimal visit frequency correlates with disease severity and stability. Stable patients benefit from quarterly check-ups, while those with severe COPD require monthly monitoring. Each appointment includes spirometry testing, medication review, and treatment plan adjustments.
Post-exacerbation visits within 7 days reduce hospital readmission rates by 35%. Telehealth options now supplement in-person care, offering convenient monitoring for 64% of stable patients between regular visits.
What emergency signs should caregivers watch for in elderly COPD patients?
Life-threatening symptoms demand immediate medical response. Key warning signs include:
• Severe breathing difficulties unresponsive to rescue medications
• Sharp chest pain or persistent pressure
• Mental confusion or sudden behavioral changes
• Bluish discoloration of lips or fingernails (cyanosis)
• Thick, dark, or bloody mucus
• Heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute at rest
• Sudden ankle or leg swelling
Early recognition of these symptoms leads to 40% better outcomes when treated promptly. Caregivers should maintain an emergency action plan and keep important medical information readily accessible.
Conclusion
Managing COPD in elderly patients requires a strategic, holistic approach that delivers measurable results. Clinical data shows that 67% of seniors who follow thorough treatment plans experience significant improvements in their daily activities. These plans typically combine:
- Personalized medication protocols
- Structured pulmonary rehabilitation exercises
- Strategic lifestyle modifications
- Regular health monitoring
Research demonstrates that age no longer serves as a limiting factor in COPD treatment success. Elderly patients who actively engage in their care plans achieve remarkable outcomes – 42% report enhanced mobility and 58% note improved breathing capacity.
Pulmonary rehabilitation programs prove particularly effective, with participants experiencing an average 31% increase in exercise tolerance and respiratory muscle strength.
The cornerstone of successful COPD management lies in strong partnerships between medical teams, patients, and caregivers.
When these collaborative relationships focus on consistent monitoring and lifestyle optimization, elderly patients maintain greater independence. While COPD presents ongoing challenges, evidence-based management strategies enable 73% of seniors to participate in regular social activities and maintain meaningful connections well into their advanced years.



